In ground water, as well as some surface waters, the most significant inorganic species of Arsenic (As) of concern are Arsenite (As3+) and Arsenate (As5+).
As5+ is easier to remove/filter from than As3+. Therefore, if there is a known quantity of Arsenic in your water, knowing it’s oxidation state is essential information for it’s effective removal.
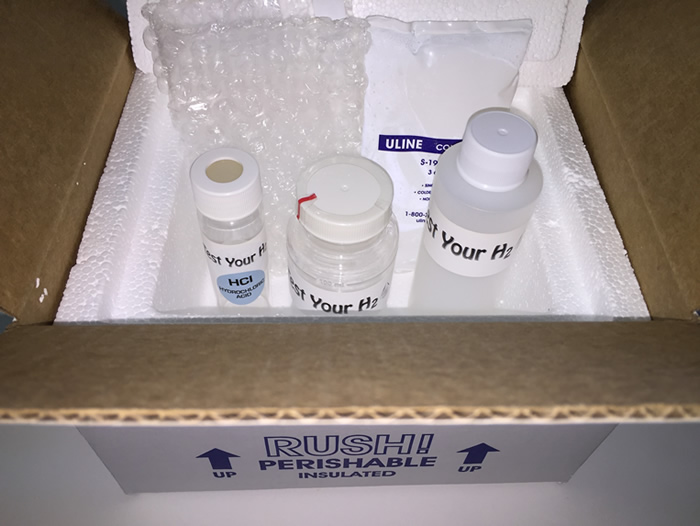
Sample Kit Shipping, Turnaround Time, and Reporting
Once you place your order, you will receive your water testing kit within 5-7 business days. Follow the water sampling instructions included in the kit and return the kit using the pre-paid return shipping label.
Once your sample is received by our laboratory, you will receive your results within 5-working days.
Your analytical data reports are emailed in .pdf format.
Note: The reported analytical data contained within the arsenic speciation water test report are NOT to be used for compliance purpose.